|
|
9 tahun lalu | |
|---|---|---|
| Godeps | 9 tahun lalu | |
| conf | 9 tahun lalu | |
| doc | 9 tahun lalu | |
| src | 9 tahun lalu | |
| test | 9 tahun lalu | |
| vendor | 9 tahun lalu | |
| .gitignore | 9 tahun lalu | |
| .travis.yml | 9 tahun lalu | |
| LICENSE | 10 tahun lalu | |
| Makefile | 9 tahun lalu | |
| Makefile.cross-compiles | 9 tahun lalu | |
| README.md | 9 tahun lalu | |
| README_zh.md | 9 tahun lalu | |
| cross_compiles_package.sh | 9 tahun lalu |
README.md
frp
What is frp?
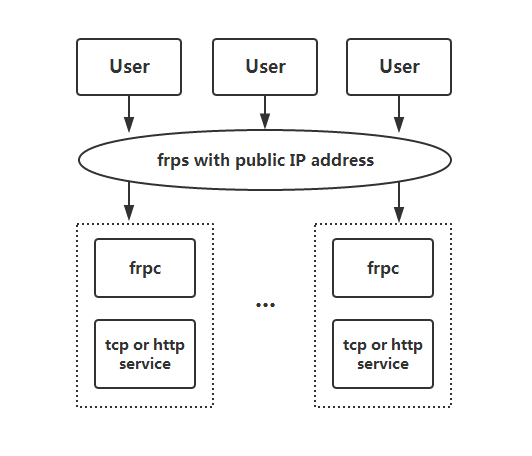
frp is a fast reverse proxy to help you expose a local server behind a NAT or firewall to the internet. Now, it supports tcp, http and https protocol when requests can be forwarded by domains to backward web services.
Catalog
- What can I do with frp?
- Status
- Architecture
- Example Usage
- Features
- Development Plan
- Contributing
- Contributors
What can I do with frp?
- Expose any http and https service behind a NAT or firewall to the internet by a server with public IP address(Name-based Virtual Host Support).
- Expose any tcp service behind a NAT or firewall to the internet by a server with public IP address.
- Inspect all http requests/responses that are transmitted over the tunnel(future).
Status
frp is under development and you can try it with latest release version. Master branch for releasing stable version when dev branch for developing.
We may change any protocol and can't promise backward compatible. Please check the release log when upgrading.
Architecture
Example Usage
Firstly, download the latest programs from Release page according to your os and arch.
Put frps and frps.ini to your server with public IP.
Put frpc and frpc.ini to your server in LAN.
Communicate with your computer in LAN by SSH
Modify frps.ini, configure a reverse proxy named [ssh]:
# frps.ini [common] bind_port = 7000 [ssh] listen_port = 6000 auth_token = 123Start frps:
./frps -c ./frps.ini
Modify frpc.ini, set remote frps's server IP as x.x.x.x:
# frpc.ini [common] server_addr = x.x.x.x server_port = 7000 auth_token = 123 [ssh] local_port = 22Start frpc:
./frpc -c ./frpc.ini
- Connect to server in LAN by ssh assuming that username is test:
ssh -oPort=6000 test@x.x.x.x
Visit your web service in LAN by custom domains
Sometimes we want to expose a local web service behind a NAT network to others for testing with your own domain name and unfortunately we can't resolve a domain name to a local ip.
Howerver, we can expose a http or https service using frp.
Modify frps.ini, configure a http reverse proxy named [web] and set http port as 8080, custom domain as
www.yourdomain.com:# frps.ini [common] bind_port = 7000 vhost_http_port = 8080 [web] type = http custom_domains = www.yourdomain.com auth_token = 123Start frps:
./frps -c ./frps.ini
Modify frpc.ini and set remote frps server's IP as x.x.x.x. The
local_portis the port of your web service:# frpc.ini [common] server_addr = x.x.x.x server_port = 7000 auth_token = 123 [web] type = http local_port = 80Start frpc:
./frpc -c ./frpc.ini
Resolve A record of
www.yourdomain.comto IPx.x.x.xor CNAME record to your origin domain.Now visit your local web service using url
http://www.yourdomain.com:8080.
Features
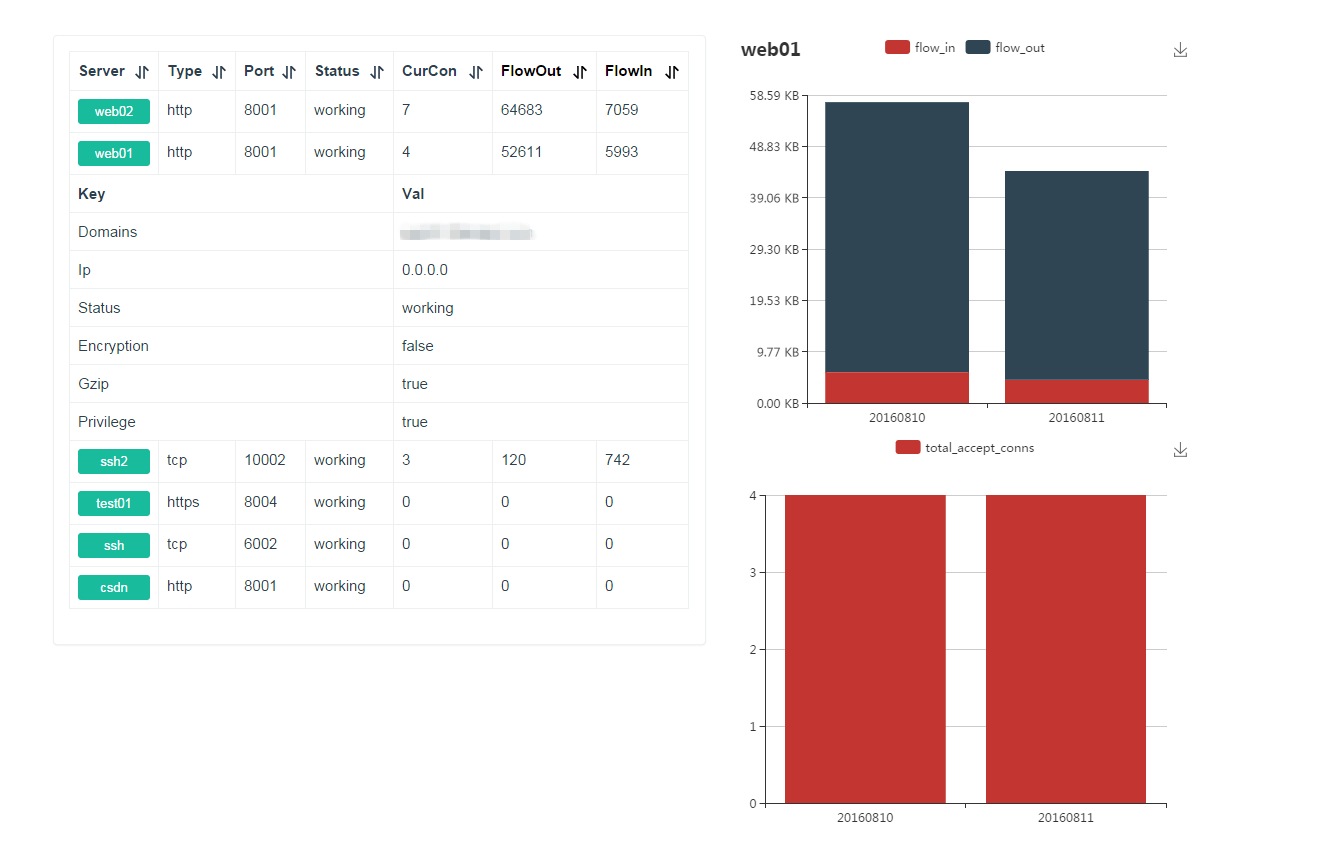
Dashboard
Check frp's status and proxies's statistics information by Dashboard.
Configure a port for dashboard to enable this feature:
[common]
dashboard_port = 7500
# dashboard's username and password are both optional,if not set, default is admin.
dashboard_username = abc
dashboard_password = abc
Then visit http://[server_addr]:7500 to see dashboard, default username and password are both admin.
Authentication
auth_token in frps.ini is configured for each proxy and check for authentication when frpc login in.
Client that want's to register must set a global auth_token equals to frps.ini.
Note that time duration bewtween frpc and frps mustn't exceed 15 minutes because timestamp is used for authentication.
Encryption and Compression
Defalut value is false, you could decide if the proxy will use encryption or compression whether the type is:
# frpc.ini
[ssh]
type = tcp
listen_port = 6000
auth_token = 123
use_encryption = true
use_gzip = true
Reload configures without frps stopped
If your want to add a new reverse proxy and avoid restarting frps, you can use this function:
dashboard_portshould be set in frps.ini:# frps.ini [common] bind_port = 7000 dashboard_port = 7500Start frps:
./frps -c ./frps.ini
Modify frps.ini to add a new proxy [new_ssh]:
# frps.ini [common] bind_port = 7000 dashboard_port = 7500 [new_ssh] listen_port = 6001 auth_token = 123Execute
reloadcommand:
./frps -c ./frps.ini --reload
- Start frpc and [new_ssh] is available now.
Privilege Mode
Privilege mode is used for who don't want to do operations in frps everytime adding a new proxy.
All proxies's configurations are set in frpc.ini when privilege mode is enabled.
Enable privilege mode and set
privilege_token.Client with the sameprivilege_tokencan create proxy automaticly:# frps.ini [common] bind_port = 7000 privilege_mode = true privilege_token = 1234Start frps:
./frps -c ./frps.ini
Enable privilege mode for proxy [ssh]:
# frpc.ini [common] server_addr = x.x.x.x server_port = 7000 privilege_token = 1234 [ssh] privilege_mode = true local_port = 22 remote_port = 6000Start frpc:
./frpc -c ./frpc.ini
- Connect to server in LAN by ssh assuming username is test:
ssh -oPort=6000 test@x.x.x.x
Port White List
privilege_allow_ports in frps.ini is used for preventing abuse of ports in privilege mode:
# frps.ini
[common]
privilege_mode = true
privilege_token = 1234
privilege_allow_ports = 2000-3000,3001,3003,4000-50000
privilege_allow_ports consists of a specific port or a range of ports divided by ,.
Connection Pool
By default, frps send message to frpc for create a new connection to backward service when getting an user request.If a proxy's connection pool is enabled, there will be a specified number of connections pre-established.
This feature is fit for a large number of short connections.
Configure the limit of pool count each proxy can use in frps.ini:
# frps.ini [common] max_pool_count = 50Enable and specify the number of connection pool:
# frpc.ini [ssh] type = tcp local_port = 22 pool_count = 10
Rewriting the Host Header
When forwarding to a local port, frp does not modify the tunneled HTTP requests at all, they are copied to your server byte-for-byte as they are received. Some application servers use the Host header for determining which development site to display. For this reason, frp can rewrite your requests with a modified Host header. Use the host_header_rewrite switch to rewrite incoming HTTP requests.
# frpc.ini
[web]
privilege_mode = true
type = http
local_port = 80
custom_domains = test.yourdomain.com
host_header_rewrite = dev.yourdomain.com
If host_header_rewrite is specified, the Host header will be rewritten to match the hostname portion of the forwarding address.
Development Plan
- Support udp protocol.
- Support wildcard domain name.
- Url router.
- Load balance to different service in frpc.
- Debug mode for frpc, prestent proxy status in terminal.
- Inspect all http requests/responses that are transmitted over the tunnel.
- Frpc can directly be a webserver for static files.
- Full control mode, dynamically modify frpc's configure with dashboard in frps.
- P2p communicate by make udp hole to penetrate NAT.
Contributing
Interested in getting involved? We would like to help you!
- Take a look at our issues list and consider submitting a patch
- If you have some wanderful ideas, send email to fatedier@gmail.com.
Note: We prefer you to give your advise in issues, so others with a same question can search it quickly and we don't need to answer them repeatly.